Sunscreen is an essential part of any skincare routine, but it’s important to be aware of the potential side effects before using it. While sunscreen is generally safe for most people, there are some potential side effects that can range from mild to severe.
This article will explore the different types of side effects that can occur from using sunscreen, how to reduce the risk of side effects, and sunscreen safety tips.
Common Side Effects of Sunscreen
Sunscreen is an essential part of any skincare routine, but it’s important to be aware of the potential side effects before using it. While sunscreen is generally safe for most people, there are some common side effects that can occur, such as skin irritation, breakouts, pilling, white cast, and allergic reactions.
Skin Irritation
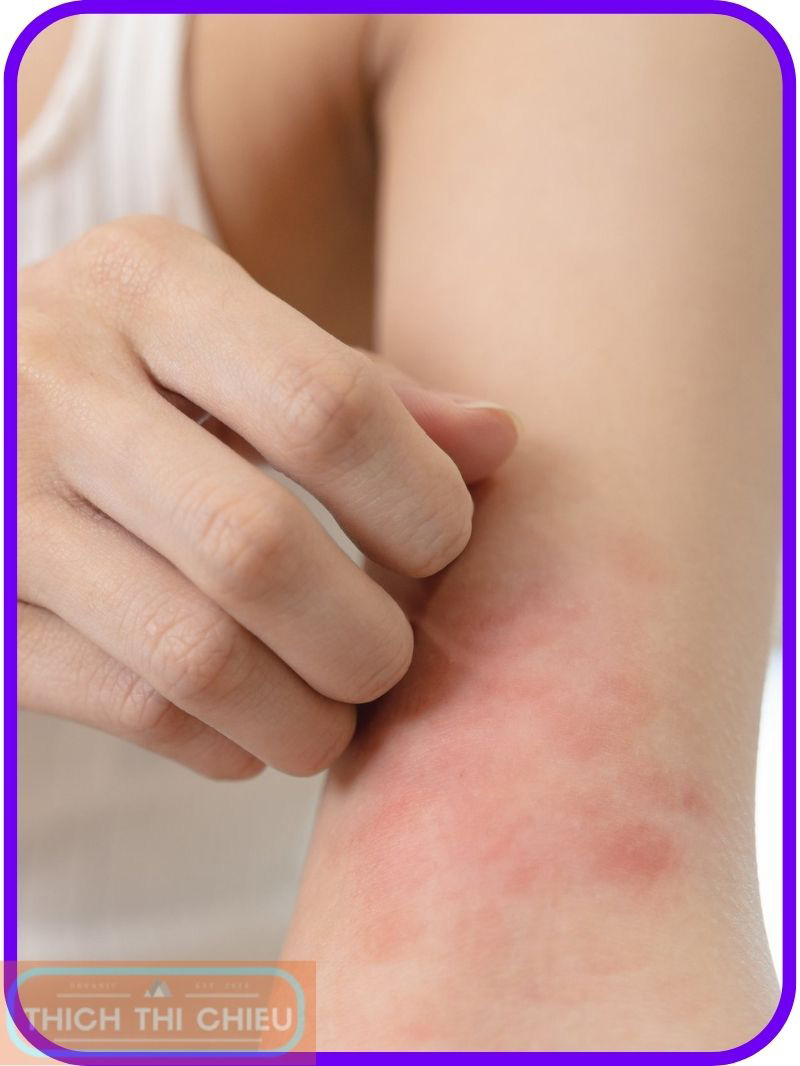
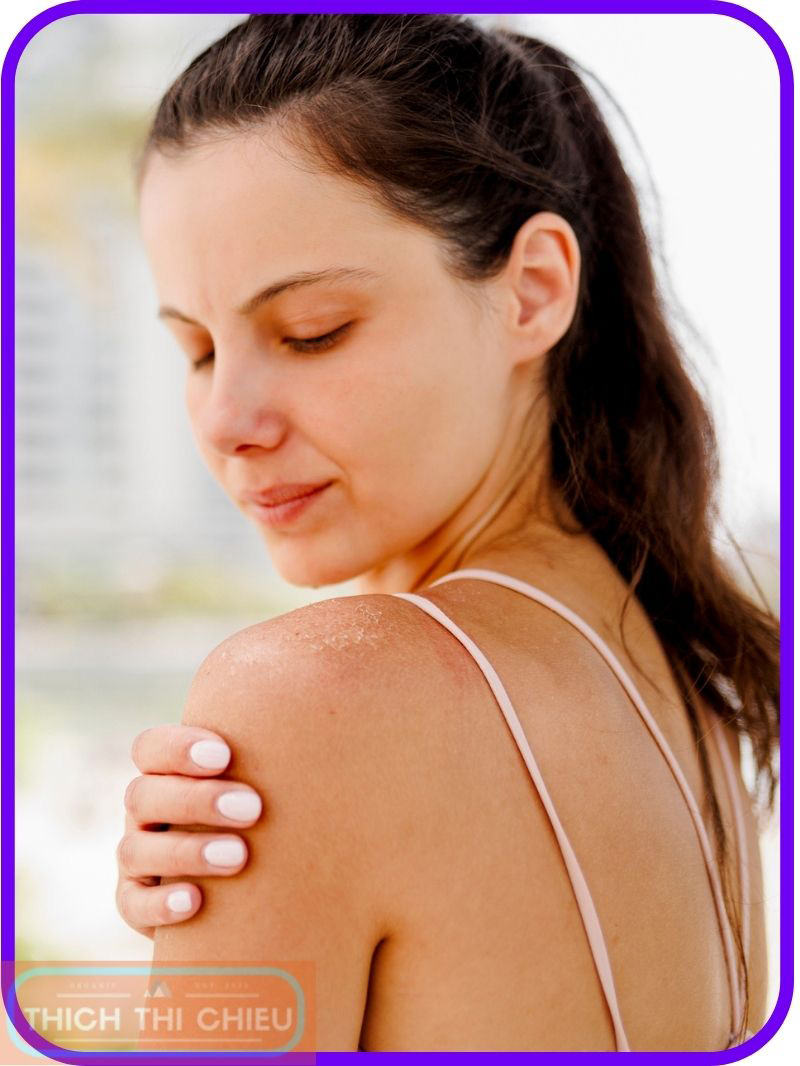
Skin irritation is the most common side effect of sunscreen. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including the type of sunscreen you use, your skin type, and how often you apply it. Sunscreen ingredients that can cause skin irritation include fragrances, alcohol, and oxybenzone.
Symptoms of skin irritation from sunscreen can include redness, itching, burning, and stinging. In severe cases, skin irritation can also cause hives and swelling.
Breakouts
Some sunscreens can clog pores and lead to breakouts. This is especially true if you have oily or acne-prone skin. Sunscreen ingredients that can clog pores include comedogenic oils, such as coconut oil and olive oil.
Symptoms of breakouts from sunscreen include blackheads, whiteheads, and pimples.
Pilling
Pilling is a condition where sunscreen rolls up into small balls on the skin. This can make the skin look and feel cakey. Pilling is caused by certain sunscreen ingredients, such as zinc oxide and titanium dioxide.
To avoid pilling, apply a thin layer of sunscreen and let it dry completely before applying makeup or other skincare products. You can also try using a non-comedogenic sunscreen.
White Cast
Some sunscreens can leave a white cast on the skin, especially darker skin tones. This is caused by the way that light reflects off of the sunscreen particles. White cast is most common with mineral sunscreens, which contain zinc oxide and titanium dioxide.
To avoid white cast, choose a sunscreen that is labeled as “broad-spectrum” and has an SPF of 30 or higher. You can also try using a chemical sunscreen, which is less likely to leave a white cast.
Allergic Reactions
Some people may have allergic reactions to certain ingredients in sunscreen. This is most common with people who have sensitive skin. Sunscreen ingredients that can cause allergic reactions include fragrances, oxybenzone, and avobenzone.
Less Common Side Effects of Sunscreen
Sunscreen is an essential part of any skincare routine, but it’s important to be aware of the potential side effects, even if they are less common. Some less common side effects of sunscreen include photosensitivity, hormonal disruption, and cancer.
Photosensitivity
Photosensitivity is a condition in which the skin becomes more sensitive to sunlight. This can make you more likely to sunburn, even when you are wearing sunscreen. Photosensitivity can be caused by a variety of factors, including certain medications, medical conditions, and sunscreen ingredients.
Sunscreen ingredients that can cause photosensitivity include oxybenzone, avobenzone, and sulisobenzone. If you experience photosensitivity after using a sunscreen, stop using it and see a doctor.
Hormonal Disruption
Some sunscreen ingredients have been shown to disrupt hormones in the body. This is most common with estrogen-like compounds, such as oxybenzone and octinoxate.
Hormonal disruption can lead to a variety of health problems, including reproductive problems, early puberty, and thyroid problems. More research is needed to determine the long-term health effects of hormonal disruption from sunscreen ingredients.
Cancer
Some sunscreen ingredients have been linked to an increased risk of cancer. However, more research is needed to confirm this link.
One sunscreen ingredient that has been linked to cancer is oxybenzone. Oxybenzone has been shown to penetrate the skin and enter the bloodstream. It has also been shown to mimic estrogen in the body.
Another sunscreen ingredient that has been linked to cancer is retinyl palmitate. Retinyl palmitate is a type of vitamin A that is used in some sunscreens. It has been shown to increase the risk of skin cancer in animals exposed to UV light.
How to Reduce the Risk of Side Effects from Sunscreen
Sunscreen is an essential part of any skincare routine, but it’s important to be aware of the potential side effects before using it. While sunscreen is generally safe for most people, there are some things you can do to reduce the risk of side effects, such as choosing the right sunscreen for your skin type, applying it liberally and reapplying often, testing a new sunscreen on a small area of skin before using it all over your body, and seeing a doctor if you experience any side effects.
Choose the Right Sunscreen for Your Skin Type
If you have sensitive skin, look for a sunscreen that is labeled “hypoallergenic” or “fragrance-free.” If you have oily or acne-prone skin, look for a sunscreen that is non-comedogenic, meaning it won’t clog pores.
There are two main types of sunscreen: mineral and chemical. Mineral sunscreens sit on top of the skin and reflect UV rays away, while chemical sunscreens absorb UV rays and convert them into heat.
Mineral sunscreens are generally less likely to cause side effects than chemical sunscreens, but they can leave a white cast on the skin. Chemical sunscreens are less likely to leave a white cast, but they can be more irritating to the skin.
Apply Sunscreen Liberally and Reapply Often
Sunscreen should be applied liberally to all exposed skin, including the face, neck, ears, and hands. It should be reapplied every two hours, or more often if you are sweating or swimming.
Most people don’t apply enough sunscreen, which can lead to inadequate protection and sunburn. Be sure to apply sunscreen to all areas of your skin, even if they are in the shade.
Test a New Sunscreen on a Small Area of Skin Before Using It All Over Your Body
Even if you have used a sunscreen before without any problems, it’s always a good idea to test a new sunscreen on a small area of skin before using it all over your body. This will help you identify any potential allergic reactions.
To test a new sunscreen, apply a small amount to the inside of your forearm and wait 24 hours. If you experience any redness, itching, or burning, wash off the sunscreen and don’t use it.
See a Doctor if You Experience Any Side Effects from Sunscreen
If you experience any side effects from sunscreen, stop using it and see a doctor. This is especially important if you experience hives, swelling, difficulty breathing, or anaphylaxis.
Sunscreen Safety Tips
Sunscreen is an essential part of any skincare routine, but it’s important to use it safely and effectively to get the most out of it. Here are some sunscreen safety tips:
Choose a Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or Higher
Sunscreen should protect against both UVA and UVB rays. UVA rays can cause premature aging and wrinkles, while UVB rays can cause sunburn and skin cancer. Look for a sunscreen that is labeled “broad-spectrum” and has an SPF of 30 or higher.
Apply Sunscreen Liberally to All Exposed Skin, Including Your Face, Neck, Ears, and Hands
Sunscreen should be applied to all exposed skin, even on cloudy days. Be sure to apply sunscreen to your face, neck, ears, and hands. Don’t forget to apply sunscreen to the tops of your feet and the tops of your ears.
Reapply Sunscreen Every Two Hours, or More Often if You Are Sweating or Swimming
Sunscreen wears off over time, so it’s important to reapply it every two hours, or more often if you are sweating or swimming.
Wear Protective Clothing, Such as a Hat and Sunglasses, When You Are Outdoors
In addition to sunscreen, protective clothing can help to protect your skin from the sun. Wear a wide-brimmed hat to protect your face, ears, and neck. Wear sunglasses to protect your eyes from UV rays.
Seek Shade When Possible
When you are outdoors, seek shade when possible. This will help to reduce your exposure to UV rays.
Sunscreen is an essential part of any skincare routine, but it’s important to be aware of the potential side effects, both common and less common. The most common side effects are skin irritation, breakouts, pilling, white cast, and allergic reactions. The less common side effects are photosensitivity, hormonal disruption, and cancer. However, the benefits of sunscreen far outweigh the risks. By following the tips in this article, you can reduce the risk of side effects and enjoy the benefits of sun protection. Hopefully, the above article of TTC has provided you with useful information. If you have any questions or concerns, please leave a comment below.








Leave a Reply